Your gut communicates with your brain through a complex messaging system driven by your microbiome, which includes trillions of bacteria, viruses, and fungi. These microbes produce neurotransmitters like serotonin, dopamine, and GABA, influencing your mood, focus, and emotional stability. Signals travel via neural pathways such as the vagus nerve, hormonal signals, and immune responses. Maintaining a diverse, balanced microbiome supports mental clarity and resilience—exploring further reveals how lifestyle choices can optimize this crucial gut-brain connection.
Key Takeaways
- The microbiome communicates with the brain through neural pathways, especially the vagus nerve, and chemical signals like hormones and neurotransmitters.
- Microbes produce mood-related neurotransmitters such as serotonin, dopamine, and GABA, influencing emotional and cognitive states.
- Gut hormones like serotonin and cortisol travel via the bloodstream, impacting mood, stress response, and mental clarity.
- Immune signals, including cytokines from the gut, modulate brain function and emotional responses.
- Maintaining a diverse and balanced microbiome enhances effective gut-brain messaging and overall mental health.
What Is the Microbiome and Why Does It Matter for Your Brain?
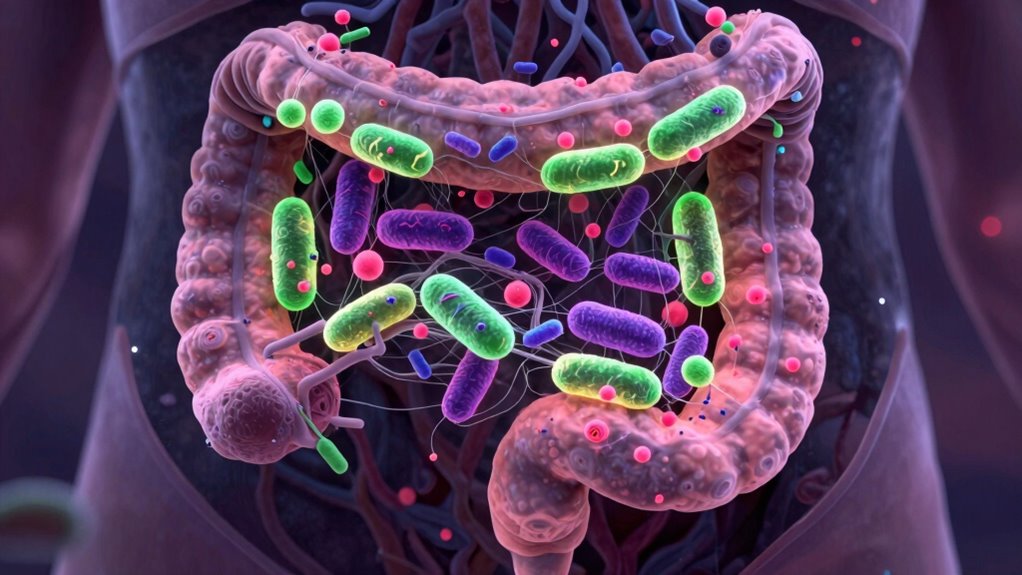
Your microbiome is a bustling community of trillions of bacteria, viruses, and fungi living mainly in your gut. This collection of microorganisms, known as your gut flora, plays a crucial role in your overall health. Microbiome diversity—the variety of different species in your gut—directly impacts how well your microbiome functions. A diverse microbiome supports digestion, immune response, and nutrient absorption. When your gut flora is balanced and varied, it helps maintain a healthy environment that influences your brain’s well-being. An imbalanced microbiome, with reduced diversity, can lead to inflammation and other issues that may affect mental health. Maintaining a diverse microbiome is essential because it’s more than just digestion; it’s a key player in your brain’s health too. Promoting microbial diversity through diet and lifestyle choices can help prevent the development of health issues related to imbalance. Additionally, emerging research suggests that microbiome composition can influence neurotransmitter production, further impacting mental health.
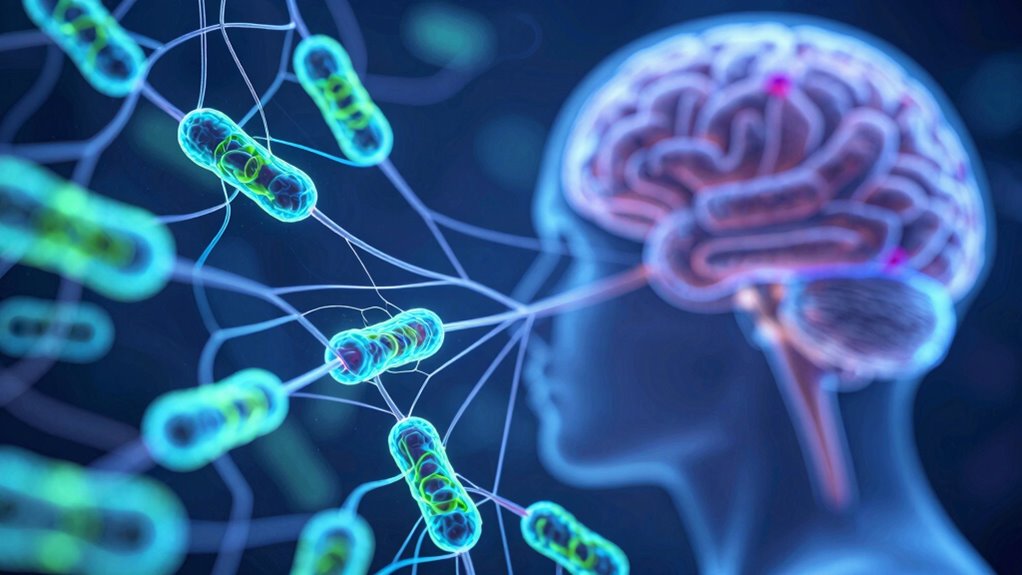
How Your Gut Communicates With Your Brain Through the Microbiome
Your gut and brain stay connected through complex pathways that involve microbiome-produced neurotransmitters. These signaling routes influence your mood and thinking, shaping how you feel and function daily. Understanding this communication can help you see how your gut health impacts your mental well-being. Recognizing the importance of European cloud innovation highlights how advanced technology can support research into the microbiome and its effects on mental health. Additionally, ongoing research into microbiome signaling pathways continues to reveal the depth of this biological dialogue, emphasizing the importance of maintaining a healthy gut. Advances in arcade game technology are also being used to develop new diagnostic tools for gut health. For instance, insights from Youngster Choice demonstrate how diverse individual factors can influence microbiome composition and its messaging. Recent studies are also exploring how microbiome diversity can affect the strength and clarity of these internal communications, further underscoring the need for holistic approaches to health.
Microbiome and Neurotransmitters
The gut microbiome actively influences brain function by producing and modulating neurotransmitters, the chemical messengers that facilitate communication between neurons. Microbiome diversity plays a pivotal role in neurotransmitter synthesis, as different bacterial species contribute uniquely to this process. For example, certain gut bacteria produce serotonin, dopamine, and gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), all essential for mood regulation, cognition, and stress response. When your microbiome is diverse, it supports balanced neurotransmitter production, which can positively impact your mental health. Conversely, reduced diversity may impair neurotransmitter synthesis, leading to issues like anxiety or depression. By fostering a rich and diverse microbiome through diet and lifestyle, you help guarantee your gut can effectively communicate with your brain via these fundamental chemical messengers.
Gut-Brain Axis Pathways
The gut-brain axis forms a complex communication network that links the gastrointestinal system with the central nervous system. You can think of it as a messaging highway, where signals travel via multiple pathways. One key route involves fiber diversity; when you consume a variety of fibers, you support a diverse microbiome, which enhances microbial balance. This balance influences how effectively your gut communicates with your brain. Microbes produce neuroactive compounds and send signals through the vagus nerve, immune system interactions, and metabolic pathways. Supporting microbiome diversity is essential for maintaining these pathways’ optimal function. By maintaining fiber diversity, you help guarantee these pathways function smoothly. This dynamic system allows your gut to send real-time updates to your brain, shaping your overall mental and physical well-being.
Impact on Mood and Cognition
Since the gut microbiome produces neuroactive compounds and communicates through multiple pathways, it plays a crucial role in shaping your mood and cognitive function. Your microbiome diversity and gut flora influence the production of neurotransmitters like serotonin and GABA, which impact how you feel and think. When your gut microbiome is balanced, you’re more likely to experience mental clarity, reduced anxiety, and emotional stability. Conversely, low microbiome diversity can contribute to depression, brain fog, and poor focus. Your gut’s health directly affects your mental well-being, and nurturing a healthy microbiome can improve your mood and sharpness. Taking steps to support microbiome diversity can enhance your mental resilience and a brighter outlook on life.
The Gut-Brain Axis: Key Pathways Connecting Your Gut and Mind
Your gut and brain communicate through direct neural pathways, like the vagus nerve, which send signals back and forth. Hormonal and immune signals also play an essential role in this connection in regulating your overall health. Additionally, ear wax odor can sometimes reflect underlying health conditions that may impact your gut-brain communication. Exploring microbiome diversity reveals how variations in gut bacteria influence mood and cognitive functions. Research indicates that gut bacteria can produce neurotransmitters that affect your brain activity. Furthermore, the composition of your gut microbiome can be influenced by diet and lifestyle choices, which in turn can modulate this communication system. Variations in microbiome composition can also be linked to different health outcomes, emphasizing the importance of maintaining a balanced gut environment. Together, these pathways form the core of the gut-brain axis, shaping how your mind and gut interact.
Neural Communication Pathways
Neural communication pathways serve as the primary routes through which your gut and brain exchange information. Vagal pathways are especially essential, acting like a direct line for signals from your gut to your brain. Neurotransmitter signaling also plays a pivotal role, with chemicals like serotonin influencing your mood and digestion. These pathways enable rapid, bidirectional communication that impacts your overall well-being.
Imagine how your gut’s health can affect your mood, stress levels, and even cravings. Feel the connection when you experience gut discomfort that shifts your mental state. Recognize how your daily choices influence this delicate network.
- Feelings of anxiety or happiness linked to gut health
- Sudden mood swings tied to digestion
- The gut’s signals influencing your mental clarity
- Stress affecting your gut’s microbiome balance
- Your emotions and gut health intertwined
Hormonal and Immune Signals
Hormonal and immune signals form essential communication channels between your gut and brain, orchestrating a complex dialogue that influences both mental and physical health. Through hormonal regulation, your gut releases hormones like serotonin and cortisol, which impact mood, stress, and digestion. These hormones travel through your bloodstream, signaling your brain and affecting emotional responses. Understanding the gut microbiome and immune modulation also plays a key role; your gut’s immune system releases cytokines and other mediators that can influence brain function and behavior. When your microbiome is balanced, it promotes healthy immune responses and stable hormonal signals. Conversely, dysregulation can lead to inflammation, mood disturbances, and cognitive issues. In essence, your gut’s hormonal and immune signals maintain a delicate balance that supports overall well-being. Additionally, emerging research suggests that battery reconditioning techniques can influence cellular health and energy efficiency, underscoring the importance of maintaining optimal system performance for overall vitality. Furthermore, the layer concepts involved in the microbiome’s organization help facilitate these complex communication pathways, ensuring efficient and targeted signaling, which highlights the significance of microbiome structure in supporting these processes. Moreover, the diverse microbial community within the gut plays a crucial role in modulating immune responses and hormone production, further emphasizing the importance of maintaining microbiome health.
Factors That Impact Your Microbiome’s Messaging to Your Brain
Several factors influence how your microbiome communicates with your brain, shaping your mental and emotional well-being. Your diet diversity plays a pivotal role; a varied diet supports a balanced microbiome that can better send positive signals. Stress management is equally essential—high stress levels can disrupt your gut’s messaging, leading to mood swings and anxiety. Other factors include sleep quality, exercise routines, and exposure to toxins, all of which can impair or enhance this communication system. When these elements are out of balance, your gut’s messaging may become muddled, affecting your mental health. Maintaining a healthy microbiome involves understanding the importance of affiliate disclosure and being mindful of how your choices impact your gut-brain connection. Paying attention to these factors helps maintain a healthy gut-brain connection, supporting emotional resilience and overall well-being. Remember, small changes can make a significant difference in your microbiome’s messaging capacity.
Simple Lifestyle Changes to Boost Your Gut-Brain Communication

Making a few simple adjustments to your daily routine can considerably enhance the communication between your gut and brain. Focus on increasing diet diversity by including a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and fermented foods. This variety promotes a healthy and balanced microbiome, which strengthens gut-brain signaling. Additionally, prioritize stress reduction techniques like meditation, deep breathing, or regular exercise. Chronic stress can disrupt your microbiome and impair messaging between your gut and brain. By combining a diverse diet with effective stress management, you support a resilient microbiome that communicates more effectively with your nervous system. Incorporating vetted products like probiotic supplements or smart home devices can further optimize your overall health and environment. Small daily changes can lead to significant improvements in your mental clarity, mood, and overall well-being by fostering ideal gut-brain interactions. For example, enhancing your microbiome diversity can significantly influence your mental health and cognitive function.
Why Understanding Your Microbiome Can Improve Your Mental Health
Understanding your microbiome is key to improving your mental health because the bacteria in your gut influence your mood, cognition, and stress levels. When you prioritize diet diversity, you feed your microbiome a wide range of nutrients, fostering beneficial bacteria that support mental well-being. Managing stress effectively reduces inflammation, helping your microbiome stay balanced. Additionally, microbiome diversity plays a crucial role in maintaining mental health by supporting a resilient and adaptable gut environment. By understanding this connection, you can take proactive steps toward better mental health. Imagine feeling calmer, more focused, and emotionally resilient simply by nurturing your gut. Your microbiome responds to your choices, so small changes can make a big difference. Microbiome health is also influenced by your lifestyle choices, further emphasizing the importance of a holistic approach.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can the Microbiome Influence Your Emotional Well-Being?
Yes, your microbiome can influence your emotional well-being. It impacts stress management and sleep quality, which are essential for mood stability. When your gut bacteria are balanced, they produce neurotransmitters like serotonin that promote happiness and calmness. Conversely, an imbalance can lead to increased stress and poor sleep, negatively affecting your emotions. Taking care of your microbiome through diet and lifestyle helps support emotional health naturally.
Are Probiotics Effective in Improving Gut-Brain Communication?
Think of probiotics as tiny messengers working to restore your gut health. They can be effective in improving gut-brain communication by promoting microbial balance, which supports your emotional well-being. When your microbiome is in harmony, it’s like a well-conducted orchestra, ensuring signals between your gut and brain flow smoothly. Incorporating probiotics may help you feel more balanced and resilient, making your gut’s messaging system work better for you.
How Quickly Can Lifestyle Changes Impact the Microbiome?
Lifestyle changes can impact your microbiome within days to weeks. Increasing fiber diversity provides different nutrients for your gut bacteria, promoting healthier diversity. Regular exercise also positively influences your microbiome, boosting beneficial bacteria and reducing harmful ones. Consistently incorporating these habits accelerates improvements, supporting better gut-brain communication. You’ll likely notice changes in digestion, mood, and overall health as your microbiome adapts to your new lifestyle.
Does Diet Have a Direct Effect on Mental Health?
Think of your diet impact on mental health as tuning a musical instrument; what you feed your body can sharpen or flatten your mood. Eating nutrient-rich foods fuels your brain and stabilizes emotions, while processed foods may cause discord. Your diet directly affects mental health by influencing neurotransmitter production and inflammation levels. So, choosing healthy options can help you maintain a more balanced, harmonious state of mind.
Can Microbiome Testing Predict Mental Health Conditions?
Microbiome testing can provide insights into your mental health by analyzing gut bacteria and microbiome diversity. While it can’t definitively predict mental health conditions, it highlights imbalances that may influence mood and anxiety. By understanding your gut bacteria, you can make targeted lifestyle changes, like diet adjustments, to support better mental well-being. Keep in mind, it’s a helpful tool but not a sole predictor of mental health outcomes.
Conclusion
Think of your microbiome as a bustling messenger, whispering secrets between your gut and brain. By nurturing this tiny army, you’re tuning into a powerful communication network that influences your mood and mental clarity. When you care for your gut, you’re opening a direct line to a healthier, happier mind. So, listen closely—your gut’s messages could be the key to revealing your best mental self. Your inner world truly holds the power to transform your mind.