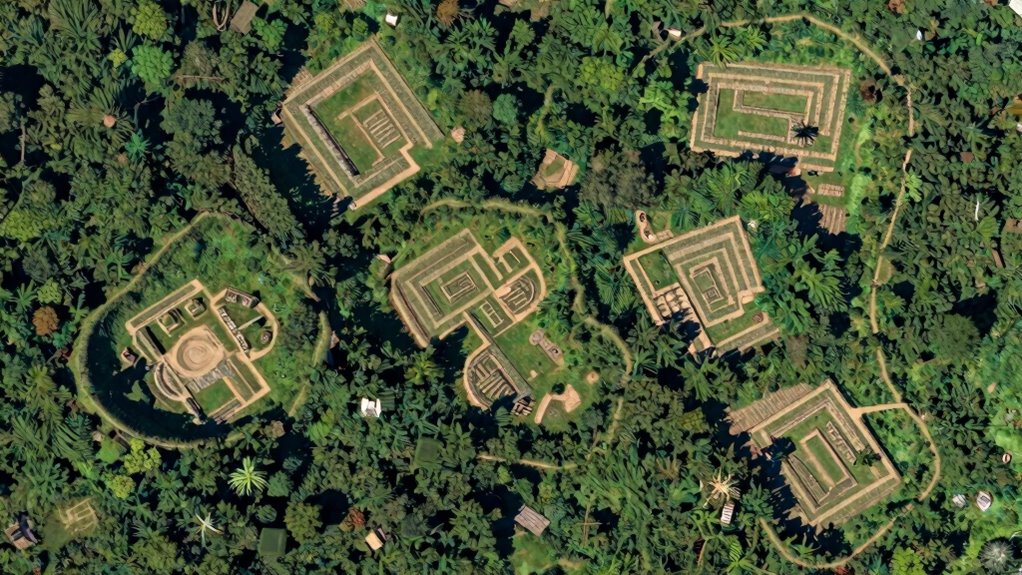
Archaeologists find “lost” cities using advanced remote sensing tools like satellite images, drones, and aerial photos. These technologies let you identify hidden structures and features beneath vegetation or soil without digging. Ground-penetrating radar and Lidar create detailed 3D maps of buried sites, revealing underground tunnels or foundations. Combining these methods improves accuracy, saves resources, and helps protect the environment. If you keep exploring, you’ll discover how these innovations revolutionize uncovering ancient civilizations.
Key Takeaways
- They utilize satellite imagery and aerial drones to identify surface features and anomalies indicating buried structures.
- Advanced remote sensing technologies like LiDAR penetrate vegetation and soil to reveal hidden city layouts.
- Ground-penetrating radar detects underground tunnels and foundations without excavation.
- Multi-sensor data integration combines different imaging methods for more accurate site identification.
- Environmental and soil analysis helps pinpoint promising locations while minimizing disturbance to the site.
Why Traditional Excavation Limits Archaeology

Traditional excavation methods have long constrained archaeologists because digging into the ground is invasive and often destructive. These methods risk damaging fragile artifacts and the context in which they’re found. Relying solely on physical digging limits what can be discovered and often results in incomplete information. However, advancements like artificial intelligence are changing this landscape. AI can analyze vast amounts of data, helping archaeologists interpret historical records more efficiently. By cross-referencing ancient texts, maps, and records, researchers can identify potential sites without disturbing the soil. This approach preserves the integrity of archaeological sites while providing valuable insights. In essence, technology is expanding what we can learn without the drawbacks of traditional excavation, making archaeology more precise and sustainable. Understanding archaeological data is crucial for developing non-invasive exploration methods that protect cultural heritage. Additionally, innovative techniques such as remote sensing and geophysical surveys are further enhancing our ability to locate buried sites without excavation. These cutting-edge tools harness advanced imaging techniques to detect underground features with minimal disruption.
How Satellite Images Help Find Lost Cities
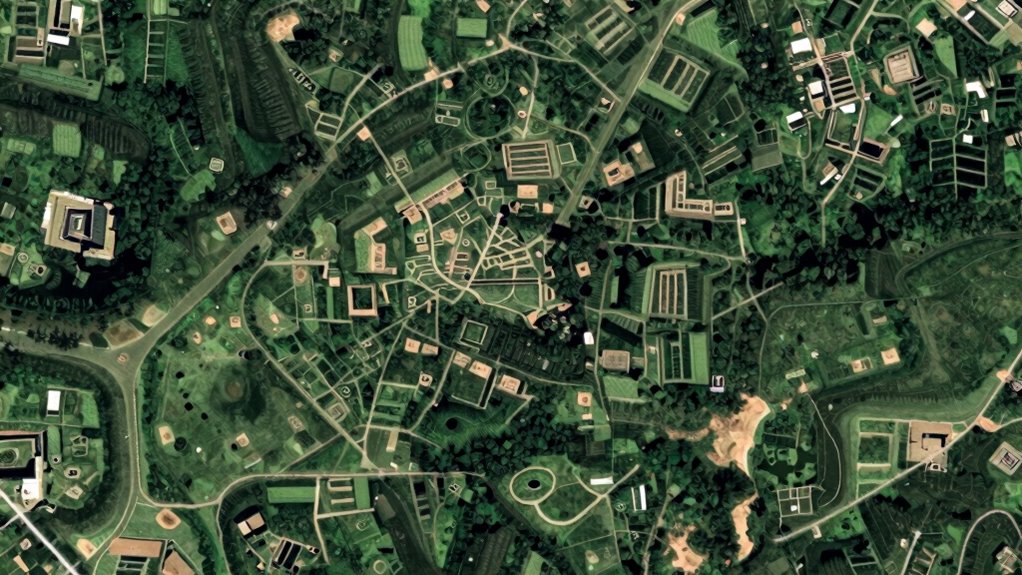

Satellite imaging has revolutionized archaeology by allowing researchers to locate lost cities from above without disturbing the ground. Satellite imagery provides a broad view, revealing subtle surface features that indicate ancient structures or settlement patterns. This technology enhances archaeological surveys by identifying potential sites that might be hidden under dense vegetation or soil. With high-resolution images, you can detect differences in vegetation health, soil discoloration, or buried foundations, all clues pointing to past human activity. These images help archaeologists prioritize locations for further investigation, saving time and resources. By integrating satellite data, you gain a powerful tool for uncovering lost cities, making exploration more efficient and less invasive. This approach transforms traditional methods, opening new pathways to understanding ancient civilizations.
Detecting Hidden Structures With Drones and Aerial Photos
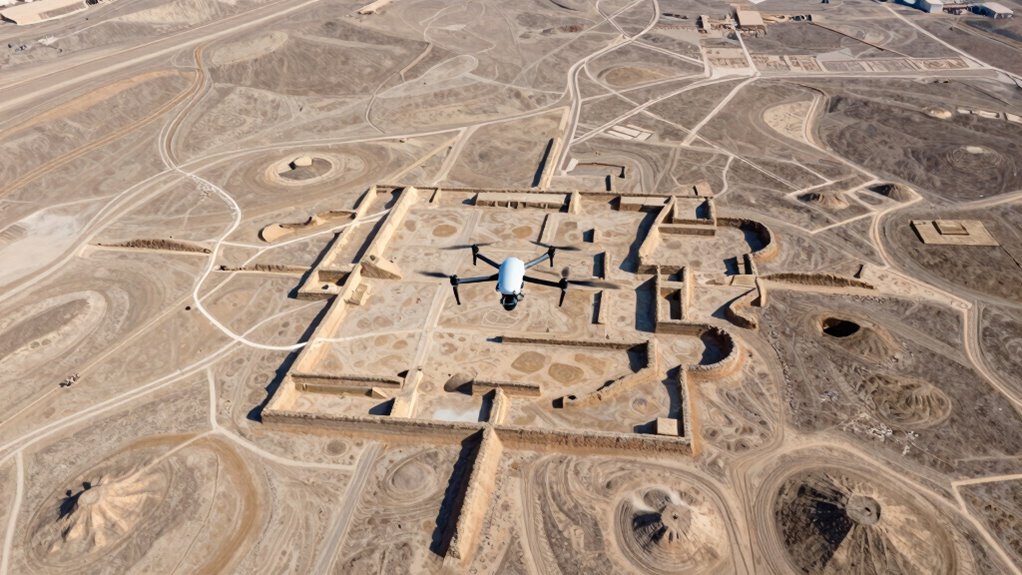

Drones and aerial photos have become essential tools for uncovering hidden structures beneath the surface. They allow you to survey large areas quickly and with high detail, revealing subtle land features often invisible from the ground. In urban planning, these tools help identify old foundations, roadways, or ruins without disturbing the site. Environmental monitoring benefits too, as aerial imagery can detect changes in vegetation or soil that suggest buried structures. By analyzing patterns, you can spot anomalies indicating past human activity or construction. This technology also enhances archaeological accuracy by providing precise data for site analysis. Additionally, the high resolution of modern aerial imagery enables the detection of small-scale features that might otherwise be missed. Using advanced imaging techniques, archaeologists can further improve their ability to identify subtle signs of buried structures. This approach saves time and resources, providing a non-invasive way to locate archaeological features. Overall, drones and aerial photos are crucial for efficiently detecting hidden structures, supporting preservation efforts, and expanding your understanding of ancient landscapes.
Using Ground-Penetrating Radar to See Beneath the Surface

Ground-penetrating radar (GPR) is a powerful tool that allows you to see beneath the surface without excavation. Using radar technology, it creates subsurface imaging that reveals buried structures, walls, and artifacts. When you employ GPR, you send electromagnetic waves into the ground, and the reflections from hidden objects are recorded to produce detailed images. This method helps you identify promising excavation sites with minimal disturbance. It also benefits from understanding the material properties of soil and rock, which influence the clarity and depth of the radar signals.]
Creating 3D Maps of Buried Sites With Lidar
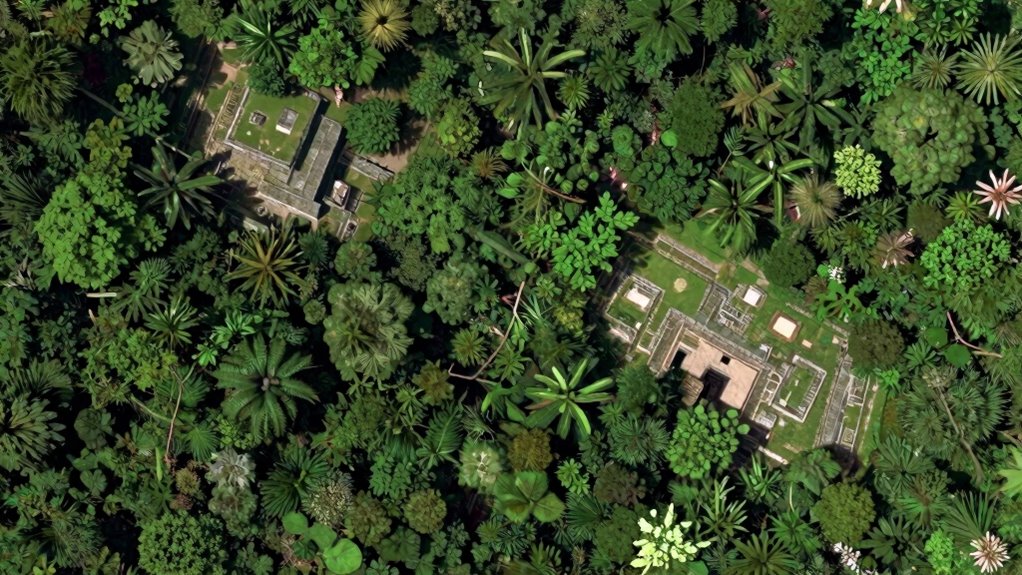

Lidar technology uses laser pulses to create detailed 3D images of buried sites from above, revealing structures hidden beneath vegetation or soil. This method allows you to see features that are otherwise impossible to detect with traditional surveys. By enhancing archaeological surveys, lidar helps uncover lost cities faster and more accurately than ever before.
Lidar Technology Basics
Lidar technology has revolutionized archaeology by allowing researchers to create detailed, three-dimensional maps of buried sites without ever lifting a trowel. Its historical context shows how technological advancements have transformed excavation methods. With lidar, you can scan large areas quickly, capturing precise elevation data from the air. This involves bouncing laser pulses off the ground and measuring their return times to build accurate models. Key aspects include:
- Emission of rapid laser pulses
- High-resolution 3D imaging
- Penetration through vegetation
- Rapid data collection
- Digital elevation models (DEMs)
These features enable you to detect subtle surface features and hidden structures beneath forest canopies or soil. Understanding these basics helps explain why lidar has become an essential tool for modern archaeology, revealing lost cities without invasive digging.
Revealing Hidden Structures
By emitting laser pulses from an aerial platform, archaeologists can create detailed three-dimensional maps that reveal hidden structures beneath dense vegetation or soil. This technique uncovers features like underground tunnels and buried artifacts without excavation. Using lidar, you can detect subtle surface changes indicating man-made structures, even when concealed. The technology’s precision allows you to visualize entire sites in remarkable detail. For example:
| Feature | Detection Method | Significance |
|---|---|---|
| Underground tunnels | Laser reflection patterns | Reveal secret pathways |
| Buried artifacts | Surface contour analysis | Identify locations for excavation |
Furthermore, lidar data can be integrated with other remote sensing techniques to enhance archaeological investigations. | Application | Advantage | Result |
| ———————- | —————————— | ————————————— |
|---|---|---|
| Mapping large areas | Rapid, non-invasive survey | Pinpointing hidden structures |
| Revealing buried features | High-resolution data | Better understanding of site layout |
Enhancing Archaeological Surveys
Enhancing archaeological surveys involves creating accurate 3D maps of buried sites, which allows you to visualize underground features in detail before excavation. Using lidar technology, you can detect subtle surface variations that reveal structures otherwise hidden. This is especially useful in underwater archaeology, where sonar-based lidar uncovers submerged ruins. It also complements historical document analysis, confirming clues from old maps or texts. With these maps, you can:
- Identify potential excavation areas more precisely
- Minimize unnecessary digging and site disturbance
- Detect buried walls, roads, and terraces
- Integrate data with GIS for exhaustive site analysis
- Share detailed visuals with remote teams or stakeholders
This approach streamlines surveys, saves time, and increases accuracy in locating lost cities without invasive methods.
Combining Remote Sensing Tools for Better Results
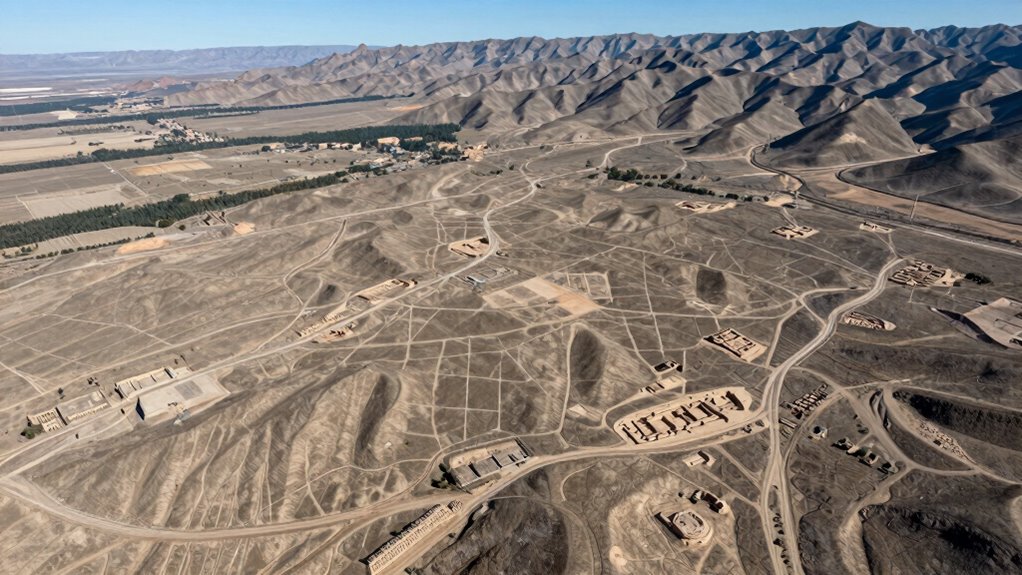

Using multiple remote sensing tools together can markedly improve the accuracy and efficiency of discovering lost cities. By integrating data from satellites, LiDAR, and ground-penetrating radar, you gain an extensive view that single methods can’t provide alone. This integrated approach allows archaeologists to interpret complex data more effectively, revealing hidden features beneath dense vegetation or soil layers. This comprehensive technique can lead to more precise site identification, saving time and resources during excavations. This approach helps identify subtle features beneath vegetation or soil, reducing false positives. Additionally, combining these methods can help you detect subtle archaeological signatures that might otherwise go unnoticed. Employing multi-sensor data analysis further enhances the ability to distinguish genuine archaeological features from noise. Moreover, advances in data processing techniques facilitate the efficient handling of large datasets, enabling more rapid insights. However, remote sensing ethics come into play; you must ensure responsible use of data, respecting local communities and avoiding damage. Effective data management is essential to handle the large volumes of information collected, allowing you to analyze and cross-reference findings efficiently. Combining tools not only speeds up discoveries but also enhances reliability, making it easier to pinpoint promising sites for further investigation while maintaining ethical standards and managing data responsibly.
Benefits of Remote Sensing: Saving Resources and Preserving Sites
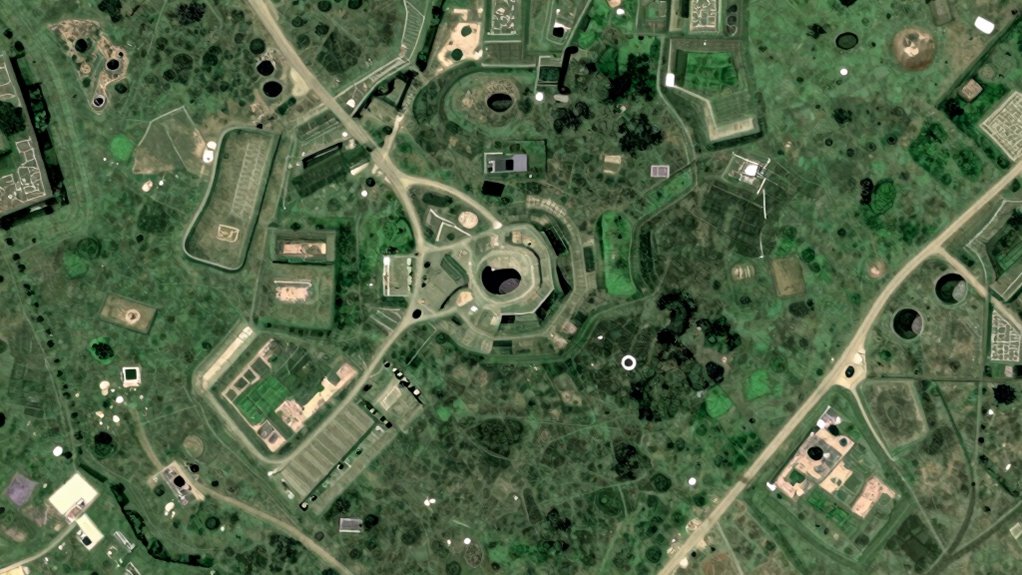

Remote sensing techniques considerably cut down on the need for extensive excavation, saving valuable resources and reducing environmental impact. This approach enables cost-effective exploration by identifying promising sites before any digging begins. You can also better protect fragile ecosystems and cultural heritage by minimizing physical disturbance. The benefits include:
- Lower excavation costs and fewer unnecessary digs
- Preservation of archaeological sites from damage
- Reduced ecological footprint during surveys
- Efficient use of resources like time and manpower
- Enhanced ability to monitor site changes over time
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are the Limitations of Remote Sensing Techniques in Archaeology?
You should know that remote sensing techniques have limitations in archaeology, especially in interpreting data. They can struggle with dense vegetation or urban areas, where signals are blocked or distorted. Cultural context matters too, as some sites may lack distinctive features visible from above or may be misinterpreted without proper background knowledge. These factors can lead to incomplete or inaccurate findings, requiring careful analysis and sometimes traditional excavation.
How Accurate Are Satellite Images in Detecting Underground Structures?
Satellite images can be quite accurate in detecting underground structures, especially with high satellite resolution and advanced underground detection techniques. You can rely on these images to identify subtle surface anomalies caused by buried features. While they’re not foolproof, improvements in technology have increased their precision, allowing you to locate potential archaeological sites with greater confidence before digging. Keep in mind, ground verification still remains essential for confirmation.
Can Remote Sensing Completely Replace Traditional Archaeological Excavation?
Nope, remote sensing can’t fully replace traditional excavation. Sure, tools like ground-penetrating radar and LiDAR technology can reveal hidden structures and save time, but they lack the human touch of digging, sampling, and interpreting artifacts. Think of remote sensing as the flashy trailer, while excavation is the full movie. Both are essential; one just can’t stand in for the other entirely.
What Environmental Factors Affect the Quality of Aerial and Drone Imagery?
Environmental factors like vegetation cover and atmospheric conditions markedly impact the quality of aerial and drone imagery. Dense vegetation can obscure archaeological features, making them harder to detect. Poor atmospheric conditions such as fog, rain, or strong winds can blur images or reduce clarity. You’ll get the best results on clear, calm days with minimal vegetation interference, ensuring your aerial surveys capture detailed, accurate data for archaeological analysis.
How Do Archaeologists Interpret Data From Different Remote Sensing Methods Together?
Did you know that combining multiple remote sensing methods increases archaeological discovery success rates by up to 60%? You interpret data from different sources through integrated analysis and data synthesis, which helps you see beyond individual images. By cross-referencing satellite imagery, LiDAR, and ground-penetrating radar, you identify subtle features and patterns. This holistic approach allows you to form a clearer picture of hidden structures, making your discoveries more accurate and efficient.
Conclusion
Remember, a picture is worth a thousand words—and in archaeology, it can reveal the secrets of lost cities without digging random holes. By harnessing satellite images, drones, ground-penetrating radar, and lidar, you can uncover hidden structures efficiently and responsibly. These tools save resources and preserve history, proving that sometimes, the best way to find the past is to look beyond the surface. As they say, “a new perspective can open doors to the past.”