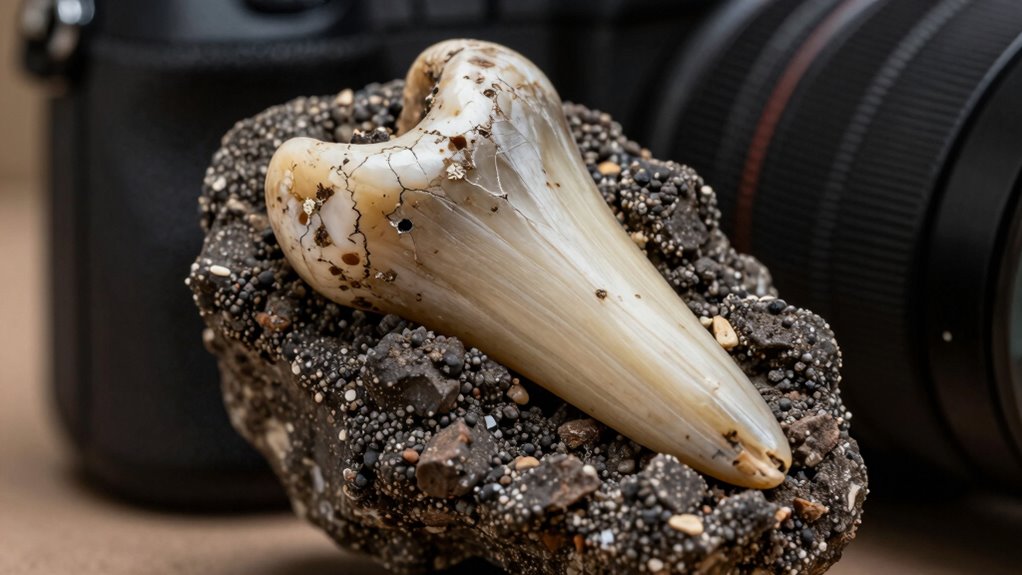
Ancient teeth are incredible time capsules that reveal a lot about your ancestors’ lives. By analyzing enamel microstructure, scientists can uncover details about diet, health, and environmental conditions during development. Isotope and DNA analysis help trace migration patterns and genetic heritage. Wear patterns and chemical signs show regional diets and food processing methods. Continue exploring to discover how these tiny fossils unseal big stories about human history and evolution.
Key Takeaways
- Teeth preserve chemical and biological information about an individual’s diet, health, and environment during their lifetime.
- Enamel microstructure records growth patterns and environmental influences, offering insights into past climates and ecosystems.
- Chemical analysis of teeth reveals ancient food sources, dietary habits, and regional environmental conditions.
- Signs of nutritional deficiencies or diseases found in teeth help reconstruct health challenges faced by past populations.
- Dental morphology and wear patterns provide clues about ancient diets, cultural practices, and migration routes.
How Do Ancient Teeth Act as Natural Time Capsules
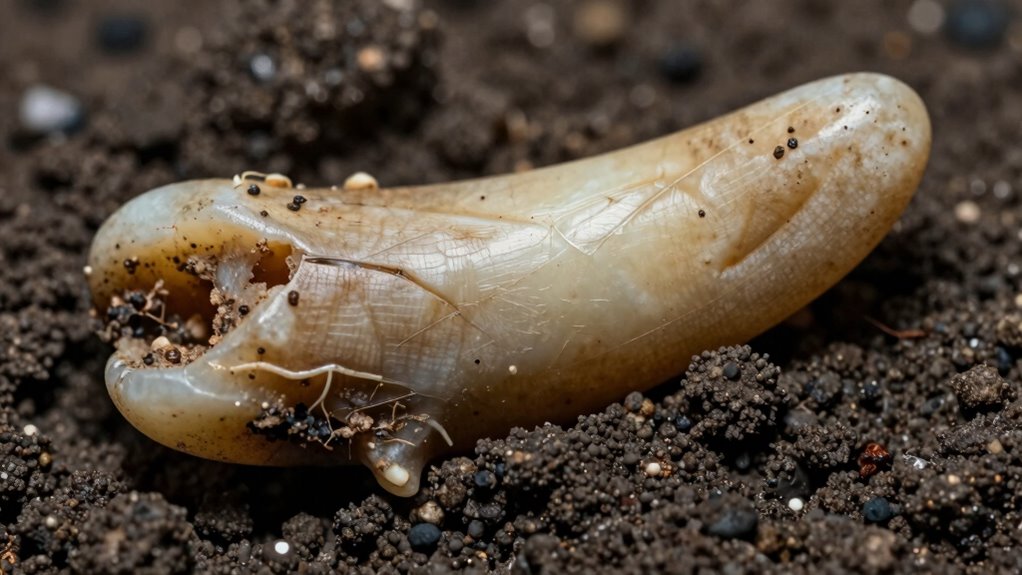

Ancient teeth serve as natural time capsules because they preserve chemical and biological information from the individual’s life. Their dental morphology, including the shape and size of the teeth, offers clues about species, age, and even evolutionary changes. The enamel microstructure is especially valuable, as it records growth patterns and environmental conditions during tooth development. These microscopic features can reveal information about diet, health, and stress experienced by the individual. Because enamel is highly mineralized and resistant to decay, it remains intact for thousands of years. By analyzing these aspects, scientists can piece together a detailed picture of ancient lives, making teeth invaluable tools for understanding our biological and cultural history.
What Can Ancient Teeth Tell Us About Diet and Nutrition
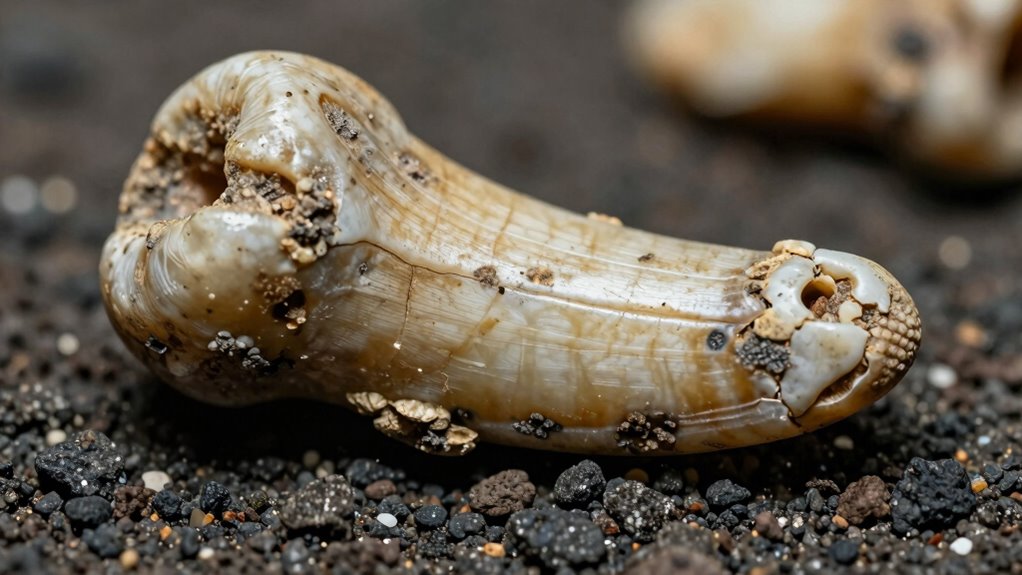

Your ancient teeth hold clues about what people ate and how their bodies absorbed nutrients. By examining enamel, scientists identify dietary signatures and spot signs of nutritional deficiencies. Additionally, the way food was processed leaves marks that reveal eating habits and technology used in ancient times. Proper food processing techniques can be inferred from these dental marks, providing further insight into ancient culinary practices. Moreover, understanding cultural dietary preferences helps researchers piece together broader social and environmental contexts of ancient populations. The analysis of dental wear and microstructures can further elucidate food preparation methods used by ancient communities. These insights are often supported by advances in microscopic analysis, which allow for more precise interpretation of dietary evidence.
Dietary Signatures in Enamel
Enamel, the hardest substance in the human body, preserves chemical clues about what people ate and drank. By examining dental wear, you can infer the types of foods consumed—hard or abrasive diets cause distinctive wear patterns. Stable isotope analysis of enamel reveals the proportions of plant versus animal intake, providing insights into ancient diets. During enamel formation, elements like carbon and nitrogen become incorporated, reflecting dietary sources. Changes in elemental ratios can indicate shifts from vegetarian to meat-heavy diets or vice versa. These chemical signatures act as dietary fingerprints, allowing you to reconstruct ancient nutrition and food processing methods. Additionally, enamel chemistry can shed light on regional dietary differences and environmental conditions that influenced food availability. Recent advances in microchemical analysis techniques enable more precise identification of dietary components within enamel, enhancing our understanding of ancient nutrition. Furthermore, the preservation of chemical signatures within enamel can also reveal information about the health and environmental stresses experienced by past populations. These chemical clues can be affected by taphonomic processes, which may alter the original signatures over time. Overall, enamel’s composition offers a direct window into the dietary habits of past populations, helping you understand their nutritional strategies and environmental interactions. Additionally, ear wax odor can sometimes reflect the body’s response to diet and health conditions, offering supplementary clues about ancient lifestyles.
Nutritional Deficiencies Evidenced
Nutritional deficiencies leave distinct marks on teeth that can reveal much about past diets and health. One key indicator is enamel hypoplasia, which appears as lines or pits on tooth enamel caused by interrupted enamel formation during childhood when nutrient shortages occur. These defects signal periods of stress related to inadequate nutrition. Dental cementum can also provide clues; changes in its deposition reflect nutritional stress over a person’s lifetime. For example, irregularities in cementum layers suggest episodes of malnutrition or illness. By analyzing these features, you can better understand how ancient populations coped with food scarcity, illness, or poor diet. Additionally, advancements in dental tissue analysis have enhanced our ability to interpret these markers with greater precision. Together, enamel hypoplasia and variations in dental cementum serve as silent witnesses to nutritional challenges faced by our ancestors.
Food Processing Effects
Ancient teeth also hold clues about how food was prepared and consumed, revealing the impact of food processing techniques on nutrition. By examining dental morphology, you can see adaptations to different diets—sharper teeth for tearing, flattened surfaces for grinding. Tooth wear patterns provide direct evidence of food texture; heavy wear suggests coarse, unprocessed foods, while less wear indicates softer, processed diets. Food processing methods like grinding grains or cooking alter how teeth interact with food, reducing wear and changing dental shapes over time. These changes tell you not only what people ate but also how they prepared their meals. Additionally, microscopic analysis of dental remains can reveal subtle details about food textures and processing techniques, offering further insights into ancient food consumption. Such studies also highlight the influence of food processing on dental health and how it shaped human evolution, providing a comprehensive view of dietary changes through history. Studying these features helps reconstruct ancient diets, showing how food processing influenced dental health and overall nutrition through history.
How Do Teeth Reveal Health and Disease in Ancient Populations
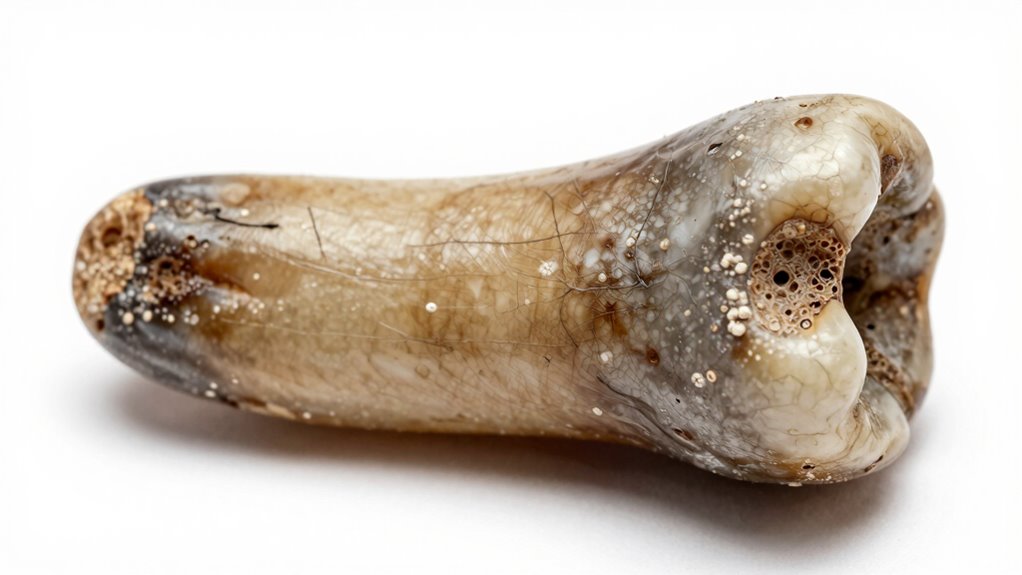
Your teeth can reveal signs of nutritional deficiencies, like enamel hypoplasia, that show when your ancestors lacked key nutrients. You might also find evidence of infectious diseases, such as lesions or abscesses, that affected their health. By studying these features, you gain insights into the health challenges faced by ancient populations. Additionally, vetted research indicates that analyzing dental wear patterns can help determine diet and lifestyle habits of past cultures. Understanding the structural features of teeth, such as enamel thickness and root morphology, further enhances our knowledge of ancient health and adaptation. Moreover, examining the microstructural composition of dental tissues can provide detailed information about metabolic conditions and environmental influences experienced by early humans. The integration of chemical analysis with morphological studies allows researchers to reconstruct ancient environments and understand how early humans adapted to their changing worlds.
Indicators of Nutritional Deficiencies
Teeth serve as biological records that reveal how diet and health affected populations long ago. When analyzing ancient teeth, you might notice signs like dental caries, which indicate a diet high in carbohydrates and sugars that promote decay. Enamel hypoplasia, on the other hand, appears as lines or pits on the enamel surface, signaling periods of nutritional stress or deficiencies during childhood. These features help you understand not just disease prevalence but also nutritional challenges faced by ancient communities. A high occurrence of dental caries suggests diets rich in processed foods or sugars, while enamel hypoplasia points to episodes of malnutrition or illness affecting tooth development. Understanding these dental markers can provide a comprehensive picture of ancient health and dietary habits. Recognizing these indicators allows researchers to interpret nutritional deficiencies more accurately and understand their impact on overall health, especially considering the influence of dietary patterns on dental health.
Evidence of Infectious Diseases
Dental health often provides clear evidence of infectious diseases that affected populations long ago. By examining teeth, you can identify signs like enamel defects and unusual tooth wear linked to infections. These clues reveal how diseases impacted individuals and communities. Specifically, look for:
- Enamel defects, indicating childhood infections affecting enamel development.
- Pitting or hypoplasia, showing periods of illness during tooth formation.
- Unusual tooth wear, which can result from infection-related inflammation or altered chewing habits.
- Abscess scars, evidence of untreated infections spreading to the jawbone.
Together, these features allow you to piece together how infectious diseases left marks on ancient populations, revealing health challenges that shaped their lives and environments.
How Is Isotope Analysis Used to Trace Migration

Isotope analysis provides a powerful tool for tracing ancient human migration by examining the chemical signatures embedded in teeth. By analyzing isotopes like strontium and oxygen, you can determine where a person lived based on regional geology and climate. For example, seafood consumption influences isotopic ratios, revealing coastal origins or trade connections. Higher social status might be inferred from specific dietary markers, such as a diet rich in marine resources, which leave distinct signatures. These chemical clues help you piece together migration patterns and interactions between different groups. By comparing isotopic data from different regions, you can identify movement across landscapes and even seasonal migrations. This method offers a direct window into ancient lives, revealing migration routes that shaped human history. Additionally, biodiversity in the environment can influence isotopic compositions, providing further context about the ecosystems people interacted with. Understanding the regional geology is crucial for accurate interpretation of isotopic data, as local rock and soil compositions directly affect the signatures found in teeth. Moreover, climate changes over time can alter isotopic signatures, making it important to consider environmental fluctuations when analyzing data.
How Does DNA Help Unlock Our Genetic Heritage From Ancient Teeth
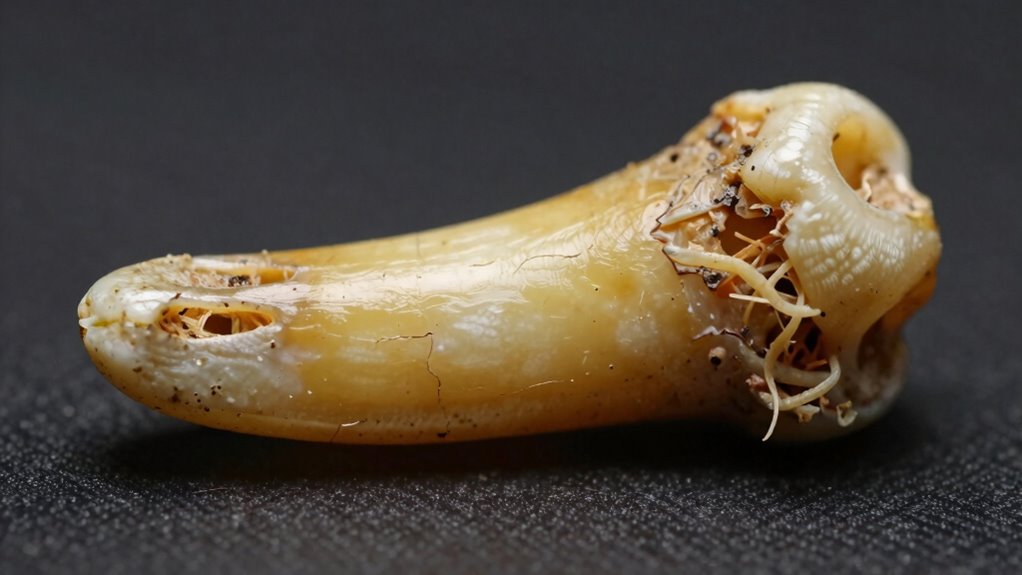

Building on how chemical signatures reveal migration patterns, analyzing DNA from ancient teeth allows you to uncover genetic relationships and ancestral origins. You can study features like dental morphology and enamel microstructure to gain insights into inherited traits. Here’s what DNA analysis reveals:
DNA analysis of ancient teeth uncovers genetic links, origins, and evolutionary dental traits.
- Genetic links between ancient populations, showing migration and interbreeding.
- Ancestral origins, helping trace migration routes.
- Evolutionary changes in dental traits over time.
- Population diversity, highlighting genetic diversity within ancient communities.
What Do Teeth Reveal About Past Environments and Climate
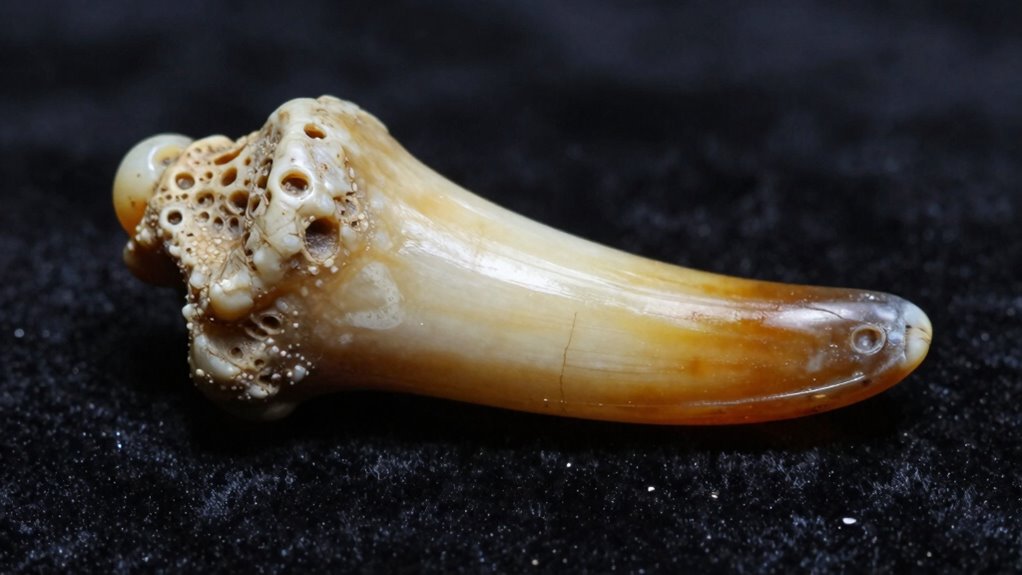

Teeth serve as natural archives of past environments and climate conditions, capturing chemical clues that reveal how ancient peoples lived and adapted. By examining dental morphology, you can identify changes in diet linked to environmental shifts, such as plant availability or climate-driven food sources. Enamel chemistry provides direct evidence of the climate and environmental influences during an individual’s lifetime. Variations in isotopic composition, like oxygen and carbon isotopes, help reconstruct temperature fluctuations and vegetation types. These insights allow you to understand how ancient populations responded to climate change, migration patterns, and resource availability. Overall, analyzing dental morphology and enamel chemistry offers a window into the ecosystems these individuals inhabited, revealing a detailed story of Earth’s changing environments across millennia.
What Techniques Do Scientists Use to Study Ancient Dental Remains
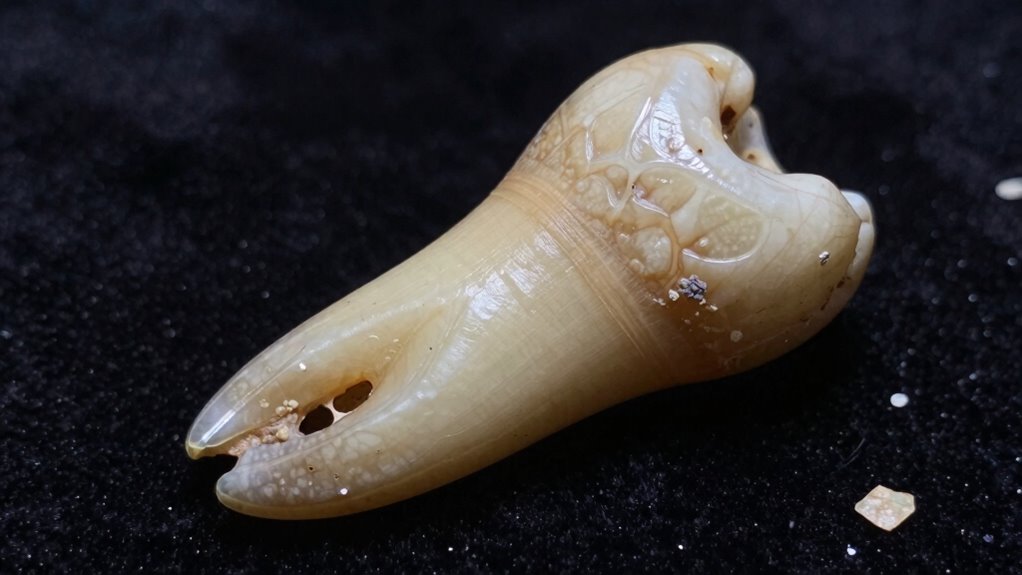

Scientists employ a variety of advanced techniques to study ancient dental remains, uncovering details about past diets, environments, and health. By examining dental morphology, you analyze the shape and structure of teeth to identify species or variations over time. Enamel microstructure reveals growth patterns and possible stresses during development. Techniques include:
Advanced techniques like micro-CT and isotope analysis reveal ancient teeth’s secrets.
- Micro-CT scanning to create detailed 3D images of tooth structures.
- Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) for high-resolution views of enamel surfaces.
- Isotope analysis to infer diet and migration patterns.
- Histological analysis of enamel microstructure, revealing growth lines and health status.
These methods allow you to decode the biological stories locked within ancient teeth, providing insights into the lives of past populations.
What Are the Main Challenges in Interpreting Data From Ancient Teeth
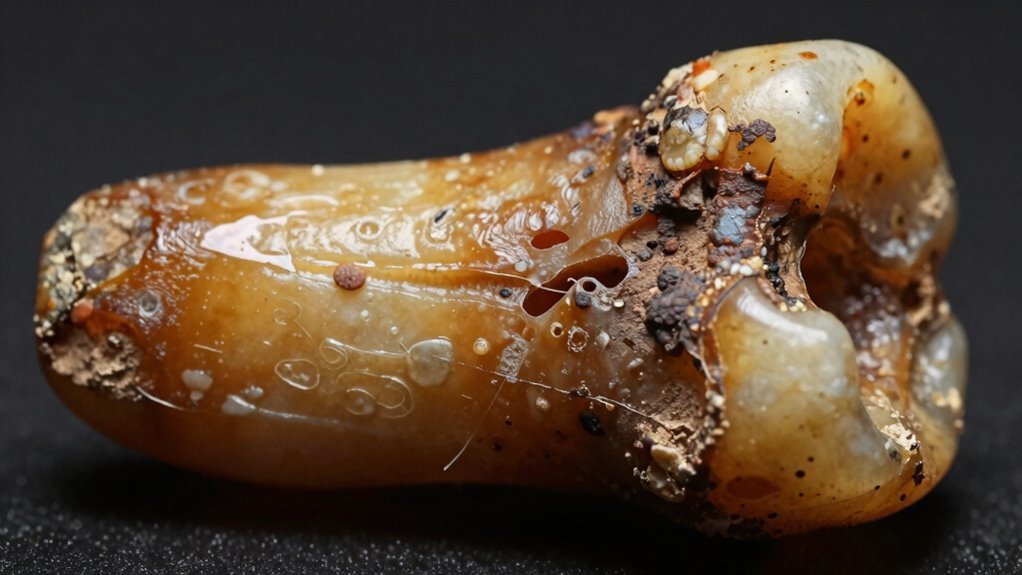

Interpreting data from ancient teeth presents several significant challenges because the preservation and context of dental remains can vary widely. One major issue is dental wear, which can obscure original features and complicate age estimates or dietary reconstructions. Additionally, enamel microstructure may degrade over time or be altered by environmental factors, making it difficult to analyze enamel quality or health indicators accurately. Preservation conditions influence the clarity of these features, affecting interpretation reliability. The table below highlights key challenges:
| Challenge | Impact |
|---|---|
| Dental Wear | Obscures original dental features, complicating analysis. |
| Enamel Microstructure | Deterioration hampers micro-level examination. |
| Preservation Conditions | Affect the overall quality of the remains. |
| Contextual Data Loss | Limits understanding of the individual’s life history. |
Why Studying Ancient Teeth Is Important for Understanding Human Evolution
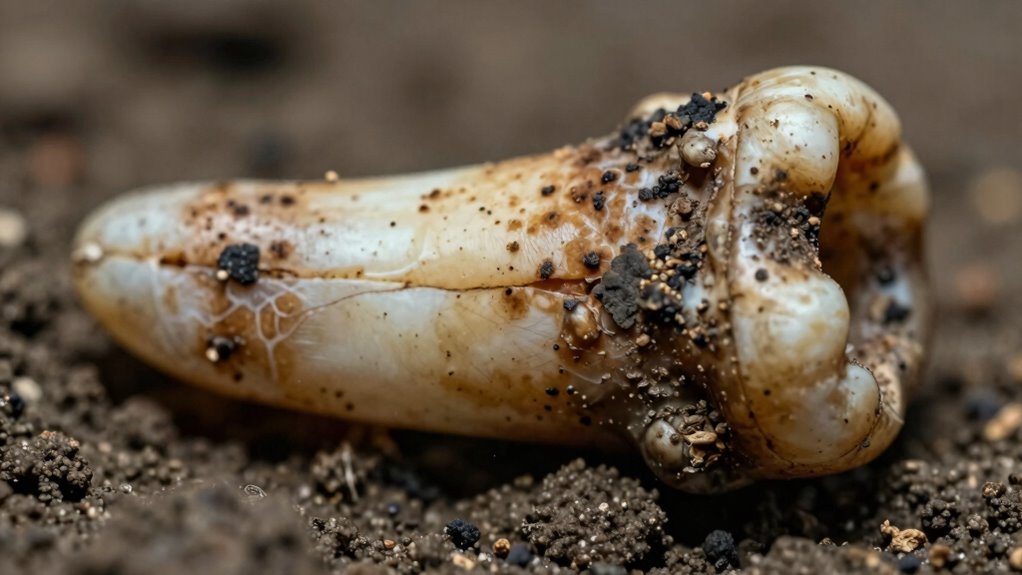

Studying ancient teeth provides crucial insights into human evolution because they preserve direct evidence of our ancestors’ biology, behavior, and environment. By analyzing dental morphology, you can identify evolutionary changes in jaw size, tooth shape, and structure that reveal adaptations over time. Tooth wear patterns indicate diet and food processing techniques, offering clues about lifestyle shifts. Here’s why it’s essential:
- Dental morphology shows how species diverged and adapted.
- Tooth wear uncovers dietary habits and environmental influences.
- Changes in enamel thickness relate to processing tougher foods.
- Fossilized teeth help track migration and interaction between populations.
These details allow you to understand how humans evolved biologically and culturally, making ancient teeth invaluable records of our past.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can Ancient Teeth Reveal Information About Ancient Pathogens and Diseases?
Yes, ancient teeth can reveal information about ancient pathogens and diseases. By analyzing the dental microbiome, you can identify ancient pathogens that affected these populations. Changes in the microbial composition often reflect disease states or infections, helping you understand how diseases spread and evolved over time. Studying these teeth offers a unique window into the health challenges faced by our ancestors, revealing insights about their diseases and immune responses.
How Accurate Are Isotope Analyses in Determining Ancient Migration Patterns?
You might think isotope analyses are perfect for tracking ancient migration, but their precision isn’t foolproof. While they provide valuable migration clues, factors like diet and environment can muddy the waters. Still, with careful sampling, isotope precision is surprisingly good, helping you piece together stories of movement across time. So, yes, it’s accurate enough to offer meaningful insights—just don’t expect it to reveal every detail flawlessly.
What Limitations Exist in Extracting DNA From Ancient Dental Remains?
You face limitations when extracting DNA from ancient dental remains due to contamination challenges and DNA degradation. Contamination from bacteria, modern DNA, or environmental sources can compromise your results, making it hard to isolate authentic ancient DNA. Additionally, over time, DNA breaks down and degrades, reducing the quality and quantity you can recover. These factors make it difficult to obtain complete, reliable genetic information from ancient teeth.
How Do Researchers Differentiate Between Dietary Signals and Environmental Contamination?
You can distinguish dietary signals from environmental contamination by carefully controlling contamination and preserving sample integrity. Researchers analyze the chemical signatures in dental remains, looking for specific isotopic patterns that match diet rather than environmental sources. They also compare these signals against known contamination markers. By maintaining strict contamination control and ensuring proper sample preservation, you can confidently interpret the ancient diet, like reading a well-preserved story etched in time.
Are There Ethical Considerations in Studying Human Teeth From Archaeological Sites?
You should consider ethical issues like obtaining proper consent protocols before studying human teeth from archaeological sites. Respect cultural sensitivities by engaging with communities and stakeholders, ensuring their perspectives are acknowledged. It’s essential to handle these specimens responsibly, balancing scientific interests with respect for the individuals and cultures involved, to avoid harm or misrepresentation. Your approach must prioritize transparency, respect, and cultural understanding throughout the research process.
Conclusion
By exploring ancient teeth, you discover a treasure trove of stories from the past, revealing how our ancestors lived, moved, and adapted. These tiny time capsules hold clues that paint a vivid picture of human history, like piecing together a complex puzzle. As you explore into their secrets, you’ll see that understanding ancient teeth isn’t just about the past — it’s about connecting the dots to our shared human journey, showing that history is truly etched in our very bones.








