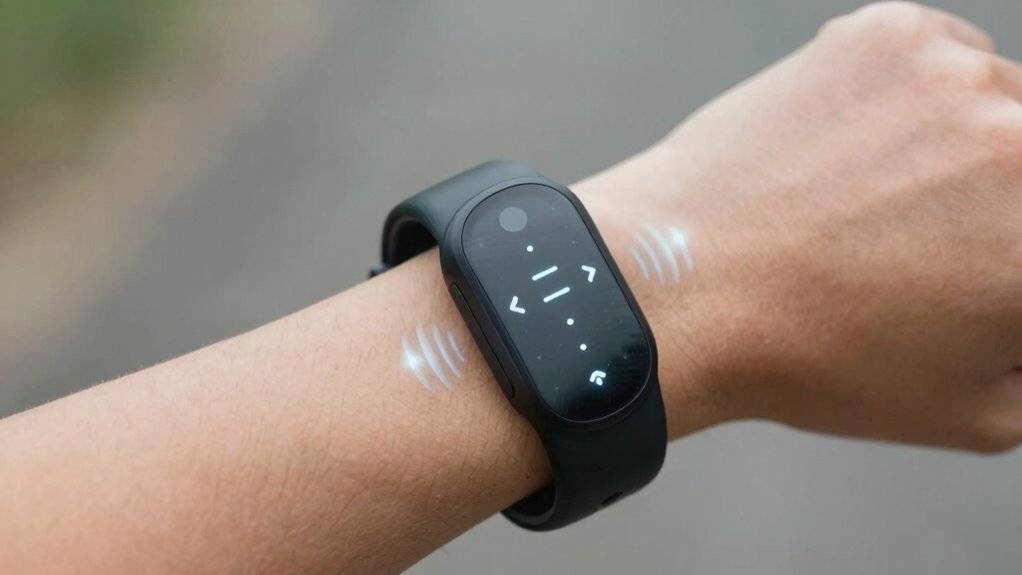
Haptic navigation uses wearable devices to turn directions into touch-based cues, replacing visual or auditory signals. These devices send vibrations or tactile patterns to your skin, guiding you discreetly and intuitively. Whether using wristbands, gloves, or armbands, you get real-time feedback for safe, hands-free navigation. This method works well outdoors and indoors, especially in noisy or crowded areas. Keep exploring to discover how these innovations can enhance your wayfinding experiences.
Key Takeaways
- Haptic wearables use tactile feedback like vibrations to convey directional cues without visual input.
- They translate GPS or environmental data into specific touch patterns for navigation guidance.
- Different vibration patterns indicate turns, alerts, or obstacles, providing discreet, real-time directions.
- These devices enhance navigation accuracy and safety, especially in environments with limited visual cues.
- Wearables integrate sensors and adaptive feedback to deliver intuitive, touch-based navigation experiences.
What Is Haptic Navigation and How Does It Work?
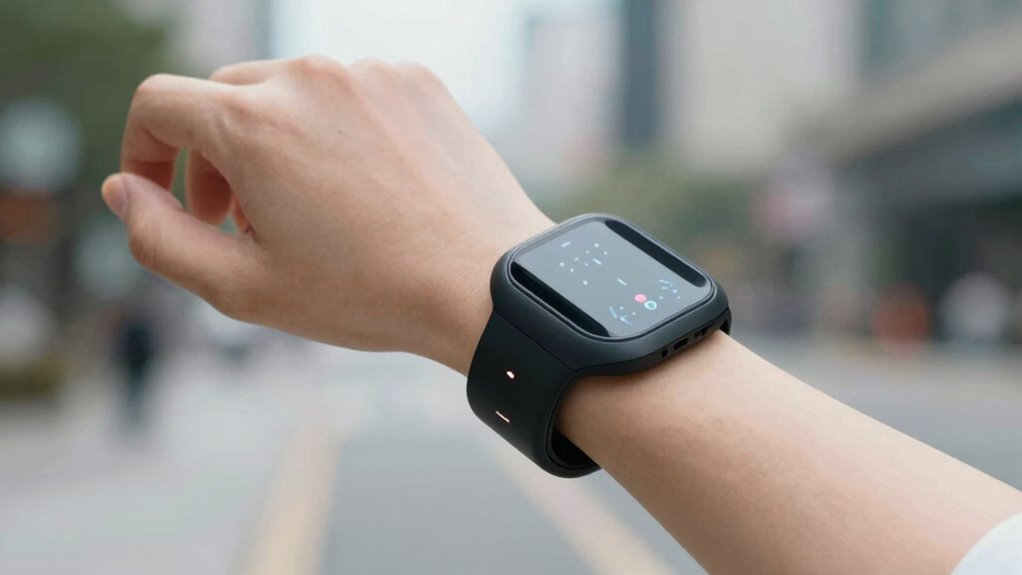

Haptic navigation is a way to guide you using touch-based feedback instead of visual or auditory cues. It works through sensory substitution, replacing sight or sound with tactile feedback that signals directions or alerts. When you wear a haptic device, it sends vibrations or pressure to specific areas of your skin, helping you interpret your environment. This tactile feedback provides real-time information, so you can navigate confidently without relying on your eyes or ears. By translating directional data into distinct touch sensations, haptic navigation enhances spatial awareness and safety. It’s especially useful for visually impaired users or in noisy environments where traditional cues might fail. Overall, this technology turns complex navigation tasks into intuitive, touch-based experiences. Additionally, integrating smart home technology can further augment navigation by providing contextual cues and environmental awareness. Incorporating feedback mechanisms can improve the clarity and effectiveness of these tactile signals, making navigation even more intuitive. Moreover, advancements in sensor technology continue to refine the accuracy and responsiveness of haptic feedback systems, broadening their applications. For example, using adaptive feedback allows the system to customize sensations based on user preferences or environmental changes, further enhancing usability. Furthermore, ongoing research into wearable devices aims to improve comfort and battery life, making haptic navigation more practical for everyday use.
Types of Wearable Devices for Haptic Navigation
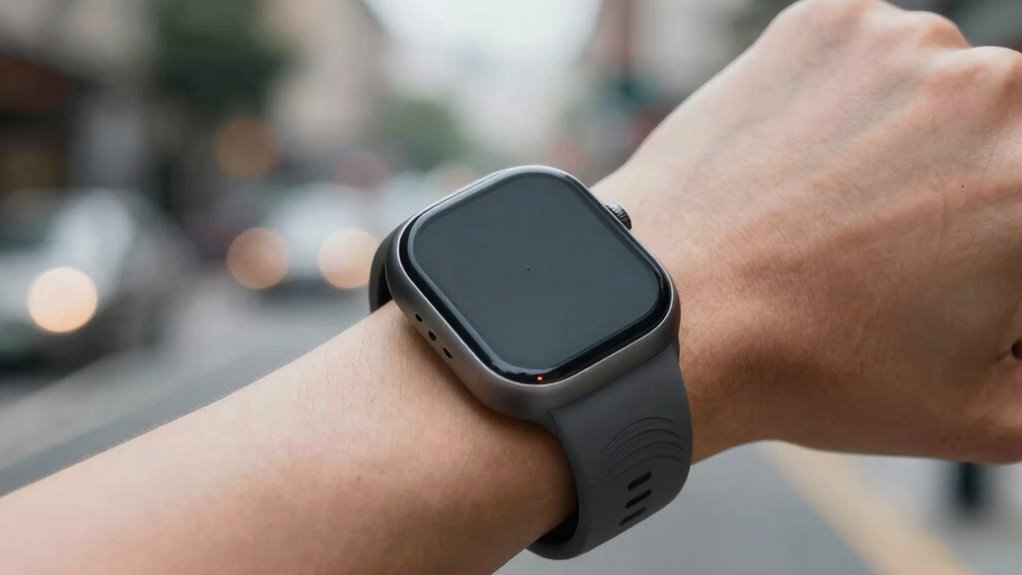

Wearable devices designed for haptic navigation come in various forms, each tailored to suit different needs and environments. You might use a wristband that provides sensory feedback through vibrations, guiding you with subtle taps. Alternatively, gloves equipped with gesture recognition technology can detect your hand movements, translating them into navigational cues. Chest straps and armbands also deliver tactile signals directly to your skin, offering discreet guidance. These devices utilize gesture recognition to interpret your gestures, such as a nod or a wave, enabling intuitive control and interaction. Sensory feedback is critical in these wearables, delivering precise, real-time cues that help you stay oriented without relying on visual or auditory cues. By combining gesture recognition with tactile signals, these devices create a seamless, hands-free navigation experience. Understanding sensory feedback is essential for optimizing the effectiveness of these wearable navigation tools, especially given the style of communication they employ. Additionally, advances in haptic technology enhance the realism and responsiveness of tactile cues, making navigation even more intuitive. Incorporating feedback mechanisms ensures that users receive accurate and timely cues, further improving navigation accuracy and safety. Improving user experience through these innovations helps users navigate more confidently in various settings.
Benefits of Turning Directions Into Touch

Turning directions into touch offers a discreet and intuitive way to navigate, especially in environments where visual or auditory cues are limited or distracting. This method provides sensory augmentation, enhancing your awareness without overwhelming your senses. Tactile feedback delivers clear, immediate cues that guide you efficiently, reducing the need to constantly check maps or listen for instructions. By converting directions into touch, you can stay focused on your surroundings while receiving reliable guidance. This approach promotes safety and confidence, particularly in crowded or noisy settings. It also supports accessibility for those with visual or hearing impairments. Additionally, choosing the right luggage & bags ensures your devices and wearable tech are protected and easily accessible during navigation. Incorporating tactile feedback technology can further improve the effectiveness of touch-based navigation systems. Moreover, integrating Free Floating concepts can lead to more adaptable and seamless user experiences, allowing for flexible interaction with your environment. Leveraging haptic technology can enhance the clarity and responsiveness of touch cues, making navigation even more intuitive. Understanding sensory augmentation can help you optimize your use of haptic navigation in various situations. Overall, turning directions into touch simplifies navigation, making it seamless, unobtrusive, and effective in a variety of situations.
How Vibrations and Patterns Guide Your Movement

Have you ever wondered how specific vibrations and patterns can direct your movement with precision? They utilize sensory substitution, replacing visual cues with tactile feedback to guide you. Different vibration patterns signal distinct directions or alerts, eliminating the need for visual input. For example, a short, sharp pulse might indicate a turn left, while a steady vibration signals to go straight. These tactile cues tap into your skin’s ability to interpret complex information quickly, enhancing navigation without relying on sight. By converting directional data into precise vibrations and patterns, wearable devices create an intuitive system that guides your movement seamlessly. This approach not only improves safety but also makes navigation accessible in environments where visual cues are limited or unavailable. sensory substitution allows users to interpret tactile signals as meaningful information, making wearable navigation more effective. Additionally, understanding how tactile feedback interacts with sensory processing helps designers optimize these devices for better user experience. Recognizing the role of net worth can also inspire innovative ways to fund and develop advanced wearable technologies, fostering growth in the Gold IRA markets.

When comparing haptic navigation to traditional GPS, you’ll notice differences in navigation accuracy and how each method fits various environments. Haptic systems often provide more immediate feedback, but may lack the detail of GPS in complex areas. Consider how your surroundings and preferences influence which option works best for you. Additionally, understanding the types of wearables that utilize haptic feedback can help you choose the most effective navigation tool for your needs. Moreover, advancements in haptic technology continue to enhance the precision and usability of these devices across different settings. As these technologies evolve, they can also adapt to different environmental conditions, improving reliability in diverse situations. Incorporating sensor integration further boosts their responsiveness and accuracy in real-world scenarios.
Navigation Precision Differences
While traditional GPS provides accurate location data, its reliance on visual cues can sometimes lead to missed turns or details, especially in complex environments. Haptic navigation offers enhanced navigation accuracy by delivering tactile cues that adapt through sensory adaptation, maintaining consistent signals without overwhelming your senses. This tactile feedback can be more precise in guiding you through crowded or unfamiliar areas, reducing reliance on visual confirmation. The difference in navigation precision becomes clear when comparing the two methods:
| Feature | Traditional GPS | Haptic Navigation |
|---|---|---|
| Sensory Load | Visual cues | Tactile cues |
| Adaptation | Limited | Continuous |
| Environment | Open, predictable | Complex, busy |
| Detail Recognition | Moderate | High |
| Reliability | Varies | Consistent |
Haptic cues improve navigation accuracy by providing reliable, intuitive guidance in any environment. Additionally, integrating vintage-inspired tech can enhance the overall aesthetic and tactile experience of modern wearable devices.
User Experience Variations
Choosing between haptic navigation and traditional GPS considerably impacts your overall user experience. With haptic feedback, sensory substitution replaces visual cues with touch, allowing you to stay oriented without constantly looking at a screen. This can foster deeper emotional engagement, as you rely less on visual distractions and more on intuitive signals. You might notice that:
- Haptic systems feel more natural and less intrusive during movement
- They promote better focus on surroundings and tasks
- The experience varies based on device responsiveness and design
- Emotional engagement increases when directions are embedded in touch, creating a more immersive connection
Ultimately, your preference depends on whether you value seamless, tactile guidance or traditional visual cues, shaping how you interact with your environment.
Environmental Suitability
Determining whether haptic navigation or traditional GPS suits a given environment depends on the specific conditions and user needs. Haptic devices excel in environments with high environmental interference, such as crowded urban areas or indoor spaces, where GPS signals can weaken or drop. They are also more weather resilient, unaffected by rain, fog, or snow that may distort satellite signals. Traditional GPS, however, can struggle in tunnels, underground locations, or dense canopies, where signals are obstructed. In such scenarios, haptic feedback provides reliable guidance without dependence on external signals. Overall, for environments with environmental interference or adverse weather conditions, haptic navigation offers a more consistent, resilient option, while GPS remains effective in open, unobstructed outdoor settings. Additionally, understanding the specific technological limitations of each system can help users select the most suitable navigation method for their needs.
How to Choose the Right Haptic Navigation Wearable

When selecting a haptic navigation wearable, start by checking if it’s compatible with your devices to guarantee seamless use. Consider the types of tactile signals it offers, so you get alerts that are clear and effective for you. Also, look at the battery life to make sure it can keep up with your daily routines without frequent recharging.
Compatibility With Devices
To guarantee your haptic navigation wearable works seamlessly with your devices, it’s essential to take compatibility into account first. Ensuring good device interoperability and cross-platform compatibility helps prevent connection issues and enhances your experience.
Consider these factors:
- Verify if the wearable supports your smartphone’s operating system (iOS, Android, etc.)
- Check for compatibility with your preferred apps or navigation tools
- Confirm Bluetooth or other wireless connection standards are compatible
- Look for firmware updates that improve device interoperability
Tactile Signal Types
Choosing the right haptic signals for your navigation wearable is essential to guarantee clear and effective guidance. Tactile feedback can come in various signal types, such as vibrations, pulses, or patterns, each conveying different information. Signal encoding determines how you differentiate directions—using distinct vibration intensities, durations, or sequences helps users interpret cues quickly. For example, a quick short vibration might indicate a turn right, while a longer pulse signals a left turn. Consider how intuitive and distinguishable each tactile feedback type is for your users. The goal is to create a seamless experience where signals are easily understood without confusion. By carefully selecting tactile feedback and encoding signals appropriately, you enhance navigation clarity and user confidence.
Battery Life Considerations
Battery life is a critical factor to consider when selecting a haptic navigation wearable, as it directly impacts usability and convenience. To ensure your device meets your needs, look for models with strong battery endurance that can last through extended use without frequent charging. Focus on devices that prioritize power optimization, reducing energy consumption during navigation. Consider these key points:
- Check the device’s estimated battery life for typical daily use
- Opt for wearables with efficient power management features
- Look for quick-charging capabilities to minimize downtime
- Consider the overall battery health and replaceability options
Choosing a wearable with good battery endurance ensures reliable navigation, while power optimization extends device longevity. Balancing these factors helps you stay connected and safe without interruptions.
Real-World Uses: City Tours, Accessibility, and More

Haptic navigation technology has begun transforming how people experience city tours and improve accessibility for individuals with visual impairments. It enhances urban exploration by providing discreet, intuitive cues that guide you through bustling streets or historic districts. Tour guides can incorporate haptic devices into their experiences, offering immersive, touch-based directions that enrich storytelling. Plus, fashion integration makes these devices more stylish and comfortable, blending seamlessly with personal outfits. For visually impaired users, haptic cues become a reliable way to navigate unfamiliar environments independently. Businesses and organizations now leverage this technology to create inclusive experiences, making city exploration more accessible and engaging. As haptic navigation evolves, it’s opening new opportunities for richer, more connected interactions in urban settings.
Challenges and Limitations of Haptic Navigation Devices

Haptic navigation devices can only cover a limited sensory range, which might leave you missing important environmental cues. You also need to be aware of potential distraction risks that could divert your attention from your surroundings. Understanding these challenges helps you better evaluate when and how to rely on haptic feedback safely.
Limited Sensory Range
One of the main challenges with haptic navigation devices is their limited sensory range, which restricts the amount of environmental information they can convey at any given time. This creates sensory deprivation and limits perception, making it harder to interpret complex surroundings. You might miss important cues or nuances in your environment.
Consider these limitations:
- Only a few directions or signals can be communicated simultaneously
- Environmental details beyond the immediate vicinity are often unavailable
- Overloading haptic feedback can cause confusion or fatigue
- Limited range reduces effectiveness in unfamiliar or complex terrains
These constraints mean you must rely on other senses or tools for full situational awareness. Despite advances, the sensory range remains a significant hurdle in delivering all-encompassing navigation assistance.
Potential Distraction Risks
While haptic navigation devices aim to enhance awareness, they can also introduce distraction risks that compromise safety. You might find yourself experiencing visual distraction if you focus too much on the device’s signals, pulling your attention away from your surroundings. This can lead to missed obstacles or hazards. Additionally, sensory overload is a concern, especially if multiple signals compete for your attention, overwhelming your senses. The tactile cues, while helpful, can become confusing if not designed carefully, causing you to misinterpret directions. As a result, your focus shifts from navigation to deciphering the haptic feedback, increasing the risk of accidents. Recognizing these risks is vital to improving device design and ensuring safety during use.
Future Trends in Wearable Haptic Guidance

As wearable technology continues to evolve, future trends in haptic guidance aim to create more intuitive and seamless navigation experiences. Expect advances in sensor integration that enhance real-time feedback, making guidance more accurate and responsive. Wearables will also prioritize user customization, allowing you to tailor sensations based on personal preferences or specific environments. You might see smarter devices that adapt haptic signals dynamically, reducing distractions and improving clarity. Additionally, improved miniaturization will make devices more discreet and comfortable.
- Enhanced sensor fusion for precise directional cues
- Personalizable haptic patterns for different contexts
- Adaptive feedback that learns from your movements
- More compact, lightweight, and stylish designs

Getting started with haptic navigation can seem intimidating at first, but with some simple tips, you’ll find it becomes intuitive quickly. Begin by familiarizing yourself with gesture controls, which enable easy, touchless interactions with your device. Practice simple gestures like taps or swipes to navigate directions, gradually increasing complexity as you grow comfortable. When choosing wearables, consider fashion integration; sleek, stylish designs ensure the device complements your wardrobe and daily routine. Adjust haptic feedback strength to your preference, so alerts are noticeable but not overwhelming. Consistent use helps you build a natural sense of direction through touch, making navigation feel seamless. Remember, the more you personalize your settings, the more intuitive and integrated your haptic experience becomes.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Accurate Are Haptic Navigation Devices in Complex Environments?
Haptic navigation devices are quite accurate in complex environments, but their precision depends on sensor calibration and environmental interference. When sensors are well-calibrated, you’ll notice clearer signals, reducing errors. However, environmental factors like dense urban settings or interference can disrupt touch cues, making directions less reliable. To get the best results, guarantee your device’s sensors are regularly calibrated and be aware that certain environments may impact touch-based guidance.
Can Haptic Wearables Be Integrated With Other Navigation Tools?
Imagine your navigation tools dancing in harmony; yes, haptic wearables can be seamlessly integrated with other navigation tools. You can enjoy gesture integration and cross-platform compatibility, making your journey smoother and more intuitive. This synergy transforms your experience from a solo act into a symphony of connected technology, guiding you effortlessly through complex environments with tactile cues that feel like an extension of your own body.
Are There Privacy Concerns With Wearable Haptic Navigation Devices?
Yes, there are privacy concerns with wearable haptic navigation devices. You should be aware that these devices collect data and track your location, which could be accessed or misused if not properly secured. Always check the privacy policies and security features. By understanding how your data is collected and stored, you can better protect your privacy while enjoying the benefits of personalized, touch-based navigation.
How Long Do Battery Lives Typically Last on These Wearables?
Battery life on wearables with haptic navigation typically lasts from one to several days, depending on usage and device features. You can extend battery longevity by managing power effectively, like turning off unnecessary sensors or reducing haptic feedback intensity. Good power management practices help you enjoy continuous navigation without frequent recharging, ensuring your device stays ready for directions whenever you need them.
What Are the Costs Associated With Adopting Haptic Navigation Technology?
You’ll find that costs for adopting haptic navigation tech vary widely, with initial device prices ranging from $100 to $500. However, ongoing cost considerations include device maintenance and upgrades. For users, affordability is growing as technology advances, making it more accessible. About 60% of early adopters consider these costs justified by enhanced safety and convenience, but it’s essential to weigh these factors against your budget and specific needs.
Conclusion
Haptic navigation is revolutionizing how you find your way, turning directions into a tactile experience that’s both intuitive and hands-free. As technology advances, these wearables will become more accurate and user-friendly, opening new doors for city explorers, travelers, and those with accessibility needs. Don’t wait for the dust to settle—embrace this touch-based guidance system now, because when it comes to navigation, it’s better to be safe than sorry and stay ahead of the curve.