The microbiome-gut-brain axis is a communication network linking your gut and nervous system through microbial signals, neurochemicals, and metabolites. Your gut microbes produce chemicals like serotonin, dopamine, and GABA, which can influence your mood and brain function. This communication mainly occurs via the vagus nerve and microbial metabolites that support brain health. Maintaining a healthy microbiome through diet and lifestyle can positively affect mental well-being—if you keep exploring, you’ll uncover even more fascinating connections.
Key Takeaways
- The gut-brain axis connects the gastrointestinal system and nervous system through neural, chemical, and immune pathways.
- Gut microbes produce neurochemicals like serotonin, dopamine, and GABA that influence brain function and mood.
- The vagus nerve is a primary communication route transmitting signals between the gut microbiome and the brain.
- Microbiome composition affects mental health, with imbalances linked to anxiety, depression, and cognitive issues.
- Maintaining a healthy microbiome through diet and lifestyle supports both gut health and emotional well-being.
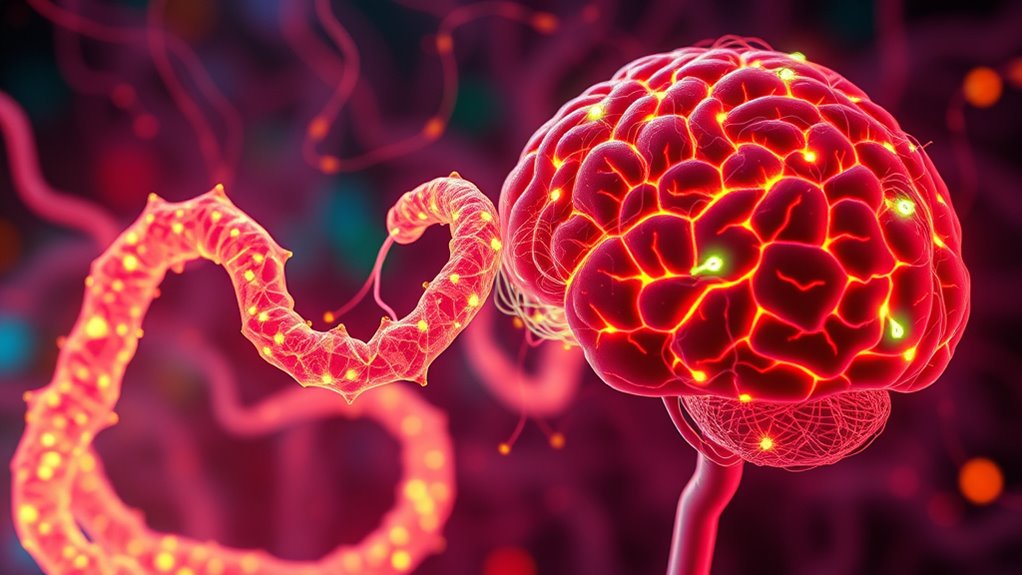
The gut-brain axis is a complex communication network that links your gastrointestinal system with your nervous system. This connection isn’t just about signals passing back and forth; it involves intricate processes like microbial communication and neurochemical influence. When you think about your gut, don’t just see it as a digestion factory—it’s a dynamic environment teeming with trillions of microbes that actively participate in your overall health. These microorganisms don’t merely sit passively; they engage in microbial communication, exchanging signals both with each other and with your body’s cells. Through these interactions, they can influence how your nervous system functions, mood, and even behavior.
Your gut microbes actively communicate and influence your nervous system, mood, and behavior through complex microbial and neurochemical interactions.
This microbial communication is fundamental because it helps regulate many bodily processes. For example, some gut microbes produce neurotransmitters like serotonin, dopamine, and gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA). These neurochemicals aren’t confined to your brain; they act locally within your gut and can also enter your bloodstream, reaching your brain and influencing your mood and mental clarity. Your microbiome essentially acts as a chemical factory, synthesizing neurochemicals that can alter neural pathways and affect your emotional states. This neurochemical influence is a key reason why gut health is often linked to mental health conditions such as anxiety and depression.
Moreover, your gut microbes communicate with your nervous system via the vagus nerve, which acts as a major highway for signals traveling between your gut and brain. When your microbiome is balanced, this communication tends to promote feelings of well-being; but when it’s disrupted, it can lead to issues like inflammation or altered neurotransmitter levels, impacting your mood and cognitive function. These microbes also release metabolites—like short-chain fatty acids—that help modulate inflammation and support the integrity of your blood-brain barrier. In doing so, they can indirectly influence neurochemical processes and brain health. Additionally, research shows that the composition of your microbiome can be shaped by dietary choices, which directly impacts microbial communication and overall health.
Understanding this bidirectional communication highlights the importance of maintaining a healthy microbiome. Your diet, lifestyle, and even stress levels shape the microbial community in your gut, which in turn can impact your mental and emotional health. Research continues to unravel how microbial communication and neurochemical influence form the foundation of this gut-brain dialogue, revealing new avenues for treating mental health disorders through microbiome modulation. So, by nurturing your gut health, you’re not just supporting digestion—you’re actively influencing your brain’s chemistry and your overall well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Does the Microbiome Influence Mental Health Disorders?
You might not realize it, but your microbiome impacts your mental health by producing microbial metabolites that influence brain function. These metabolites can affect neuroinflammation processes, which are linked to disorders like anxiety and depression. When your microbiome is balanced, it helps regulate these processes, potentially reducing mental health issues. Conversely, an imbalanced microbiome may contribute to increased neuroinflammation and worsen mental health symptoms.
Can Probiotics Effectively Modify the Gut-Brain Axis?
Like tuning a musical instrument, probiotics can help modulate your gut-brain axis. By introducing specific probiotic strains, you may enhance microbial diversity, which influences your mental health. While some studies show promising results, effects vary depending on the strains used and individual differences. So, yes, probiotics can potentially modify your gut-brain communication, but they’re not a one-size-fits-all solution—more research is needed to confirm their effectiveness.
What Role Does Diet Play in Gut-Brain Communication?
You can influence gut-brain communication through diet by including fermentation foods and dietary fibers. Fermentation foods, like yogurt and sauerkraut, introduce beneficial microbes that support gut health, while dietary fibers serve as fuel for these microbes. When you eat these, you promote a healthy microbiome, which in turn helps regulate mood, stress, and cognitive functions. So, your food choices directly impact your gut-brain connection.
Are There Specific Microbes Linked to Neurological Diseases?
You might wonder if specific microbes relate to neurological diseases. Research suggests certain microbial biomarkers are linked to neurodegenerative associations, such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s. You can influence these microbes through diet, probiotics, and lifestyle choices. While not definitive, understanding these connections helps you recognize how gut health impacts brain function, potentially guiding future therapies and early detection strategies for neurological conditions.
How Quickly Can Gut Microbiome Changes Impact Brain Function?
You might see a rapid response in your brain function after microbiome shifts, sometimes within days. Changes in gut bacteria can influence mood, cognition, and stress levels quickly, as the microbiome communicates with your brain through the gut-brain axis. So, if you adjust your diet or take probiotics, expect some effects on your mental health in a surprisingly short time, highlighting how dynamic your gut microbiome truly is.
Conclusion
As you explore the complexities of the microbiome-gut-brain axis, remember that we’re only just beginning to uncover its secrets. Every discovery raises new questions—could manipulating your gut bacteria truly influence your mind? The potential for groundbreaking treatments or unforeseen consequences hangs in the balance. Stay curious, because what we learn next might change everything you thought you knew about health, happiness, and the powerful connection between your gut and brain. The future holds surprises—are you ready to explore them?